Marine pump
-
Marine Fire Pump
-
Marine Emergency Fire Pump
-
Marine Ballast Water Pump
-
Marine Fuel Pump
-
Marine Lubricating Oil Pump
-
Marine Bilge Pump
-
Marine Sewage Pump
-
Marine Fresh Water Pump
-
Marine General Pump
-
Marine Cargo Oil Pump
-
Marine Hand Pump
-
Marine Pump Parts
-
Marine Centrifugal Pump
-
Marine Screw Pump
-
Marine Gear Pump
-
Marine Vortex Pump
-
Marine Ejector Pump
-
Marine Diaphragm Pump
-
Marine Piston Pump
-
Marine Cooling Water Pump
Chemical pump
Urban pump
Other pump
Civil Pump
Submersible Pump
Contact us
Fushi Pump Chongqing Co., Ltd
Address: No. 11, Tianxing Avenue, ShuangQiao Industrial Park, Chongqing,China
E-mail: material@hiseamarine.com
Tel: +86-23-67956606
Fax: +86-23-67956622
Mobil: +86-19332298771
CSW Marine Horizontal Centrifugal Pump
Date:2022-07-15Views:

CSW Marine Horizontal Centrifugal Pump
Overview
CSW type single-stage single-suction marine horizontal centrifugal pump is a high-efficiency and energy-saving product designed by our company referring to the performance parameters of IS type centrifugal pump, taking advantage of the horizontal pump structure, and conforming to the international standard ISO2858 and the latest Chinese standard. It is a new type of horizontal centrifugal pump that replaces conventional products such as IS type horizontal pump and DL type pump.
The flow range is 1.9 to 1450 m3/h, and the lift range is 3.36 to 156 meters. There are more than 400 specifications such as basic type, expansion type, A, B, C cutting type. According to different flow medium and temperature, we design and manufacture CSWR type hot water pump, CSW type chemical pump, CSWB type oil pump and CSWBH type explosion-proof chemical pump with the same performance parameters.
Features
1. The pump has compact structure, small volume and beautiful appearance. Its horizontal structure has a lower center of gravity, which enhances the running stability and life of the pump.
2. Easy to install. The inlet and outlet diameters are the same and are on the same centerline, which can be directly installed in any part of the pipeline like a valve. The motor and rain cover can be used outdoors. The pump is provided with mounting feet for stable installation of the pump.
3. Smooth operation, low noise and high concentricity of components. The motor adopts low-noise bearings, and is equipped with a non-stop refueling device. The pump impeller has excellent dynamic and static balance, no vibration during operation, and improves the use environment.
4. No leakage. The shaft seal adopts corrosion-resistant hard alloy mechanical seal, which solves the problem of serious leakage of the packing seal of the centrifugal pump, prolongs the service life, and ensures the clean and tidy operating site.
5. Easy to maintain. There is no need to disassemble the pipeline, just remove the pump cover nut, take out the rotor and the transmission components for maintenance.
6. According to the site conditions, the pump can be installed in horizontal, horizontal and multi-mode. According to the flow and head requirements, the parallel and series methods are used to increase the required flow and head.
Working principle
Before starting the centrifugal pump, the pump casing and the suction pipe should be filled with liquid. After starting the motor, the pump shaft drives the impeller and the liquid to rotate at a high speed. The flow channel flows into the pressurized water line of the pump. At the center of the pump impeller, as the liquid is thrown out under the action of centrifugal force, a vacuum is formed, and the water in the suction pool is pressed into the pump casing under the action of atmospheric pressure, and the impeller rotates continuously to make the liquid in the impeller. Under the action of continuous inflow and outflow, the purpose of transporting liquid is achieved.
Model Explanation CSW (R, H, B, BH)D (I) A(B, C)
CSW—CSW single-stage single-inlet marine horizontal centrifugal pump
R/H/B/BH—Hot-water pump/Chemical pump/Oil pump/Non-explosive chemical pump
D—Slow Speed of revolution
50—Inlet and outlet diameter 50 mm
160—Nominal diameter of impeller 160mm
I—Flow classification
A(B, C)—Impeller processed with 1(2, 3)cutting
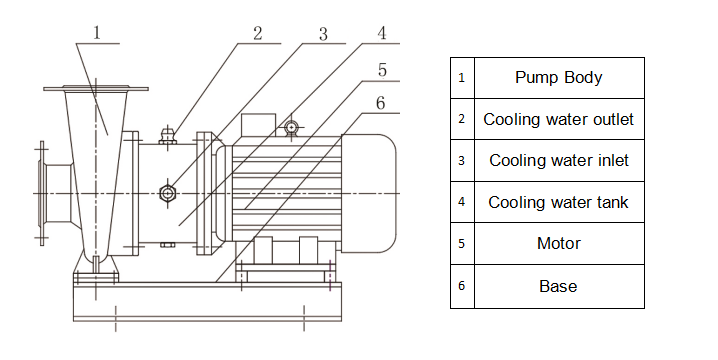
CSW type structure description:
1. The pump and the motor have the same end cover, the axial dimension is shortened, and the structure is simple.
2. The pump body is provided with a pressure-taking hole and a water-draining hole.
3. There is an exhaust valve on the pump body, which can discharge the air in the pump before working.
4. The bottom of the pump body is provided with a mounting base plate and bolt holes to ensure the stable installation of the whole unit.
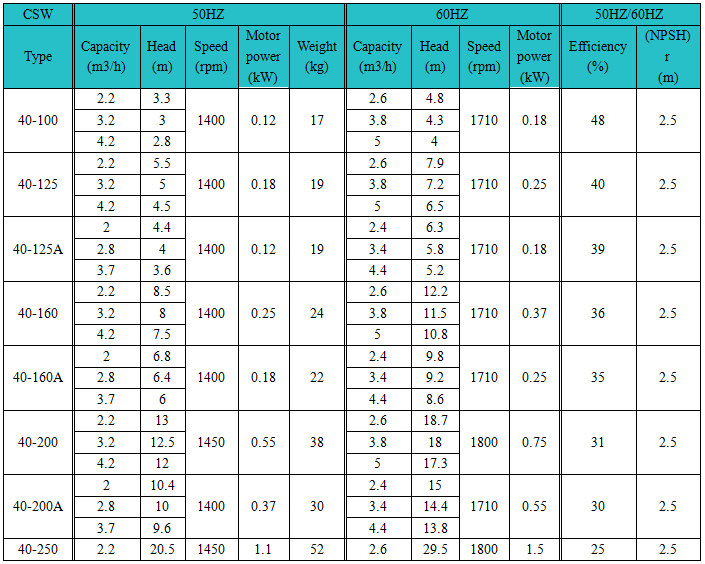
The following are only the partial parameters.In addition, please provide the parameter of the marine pump you need and we can customize the suitable type for you.
Main technical parameter
Pump Picture

The excellent design of our company's engineers, components made of high-quality materials can extend the life of the pump, reduce the frequency of maintenance, operation stability in complex environments, but it also cause different prices. If you need more details about this, you can click on the news or send an email to ask us.
Precautions for use
Preparation before starting:
1. Turn the fan blade of the motor by hand, the impeller should be free from sticking and grinding, and the rotation should be flexible.
2. Fully open the inlet valve, open the exhaust valve to fill the pump cavity with liquid, and then close the exhaust valve.
3. Check whether each part is normal: whether the bearing is well lubricated, whether the bolts of each part are tightened, whether the suction pipe is smooth, etc.
4. Manually operate the pump to allow the lubricating fluid to enter the mechanical seal face.
5. If the medium temperature is high, it should be preheated in time, and the heating rate should be 50℃/hour to ensure that all parts are heated evenly.
Start and run:
1. Fully open the inlet valve; close the outlet valve.
2. Start the motor; (pay attention to whether the direction of rotation is correct).
3. Adjust the opening of the outlet valve to meet the required working conditions. If the user is equipped with a flow meter or pressure gauge at the pump outlet, the pump should be operated at the rated point listed in the performance parameter table by adjusting the opening of the outlet valve. A flow meter or pressure gauge is installed at the pump outlet. The motor current of the pump should be measured by adjusting the opening of the outlet valve to make the motor run within the rated current. burn out. The opening size of the well-adjusted outlet valve is related to the working conditions of the pipeline.
4. Pay attention to the reading of the meter and check the leakage of the shaft seal. Normally, the leakage of the mechanical seal should be less than 3 drops/min;
Stop using:
1. When the temperature of the medium is high, it should be cooled first, the cooling rate should be <10℃/min, and the liquid temperature should drop below 80℃ before stopping.
2. Close the valve of the discharge pipeline and cut off the power supply.
3. Close the inlet valve.
4. If the pump is parked for a long time, the pump should be disassembled for cleaning and packaged for storage.
Maintenance and Disassembly
The characteristics of the pump are simple and reliable structure and durability. Under normal conditions, the pump generally does not need to be disassembled and maintained frequently. When a fault is found, it can be eliminated at any time.
1. Maintenance and maintenance during operation:
(1) The inlet pipe must be filled with liquid, and the pump is prohibited from running for a long time in the state of cavitation.
(2) Regularly check the current value of the motor during the operation of the pump, which must not exceed the rated current of the motor.
(3) After the pump runs for a long time, when the noise and vibration of the unit increase due to mechanical wear, it should be stopped for inspection, and the vulnerable parts and bearings can be replaced if necessary. The unit overhaul period is generally one year.
2. Mechanical seal maintenance and maintenance:
(1) The lubrication of the mechanical seal should be clean and free of solid particles.
(2) It is strictly forbidden for the mechanical seal to work under dry grinding conditions.
(3) Rotate the pump (motor) several times before starting, so as not to cause the graphite ring to break and damage due to sudden start.
3. Pump disassembly sequence:
A. Remove the motor or disengage the coupling.
B. Remove the bearing body assembly, check the radial clearance between the impeller and the front port ring, and check whether the impeller nut is loose.
C. Remove the impeller nut, pull out the impeller, and check the radial clearance between the impeller and the rear seal ring.
D. Loosen the set screw of the mechanical seal, pull out the moving ring part of the mechanical seal, check the fit of the end faces of the dynamic and static rings, and check the sealing condition of the "o"-shaped sealing ring (or cushion).
E. Unscrew the set nut of the coupling and pull out the coupling.
F. Remove the bearing cover and remove the pump shaft and bearing.
G. Assembly can be done in reverse order during installation.
Troubleshooting and troubleshooting
Failure | Possible causes | Solutions |
1.No water out of pump | a.Inlet and outlet valves not opened, inlet and outlet pipes jammed, or flow passage impeller jammed. b.Improper running direction of motor or low seed of motor due to open phase. c.Air leakage of suction pipe. d.Pump not filled up with liquid, or air existing inside pump. e.Insufficient inlet water supply, overhigh suction head, or water leakage at bottom valve. f.Excessive resistance of pipeline, or improper use of pump model. | a.Check and clear the jamming b.Adjust the running direction of motor, or fasten motor connections. c.Fasten the seal faces, and clear away the air. d.Open the upper cover of pump or open exhaust valve to let air completely out. e.Stop for check and adjustment (often happened to water supply pipe network and service with suction head) f.Reduce the bends of pipeline, or reselect a pump |
2.Insufficient flow of pump | a.1.Check the causes according to 1. b.Pipeline or impeller in flow passage partially jammed, scale deposited of valve. c.Voltage being low. d. Impeller worn out. | a.1.Solutions according to 1. b.Clear away the jamming, or readjust the opening of valve. c.Stabilize the voltage. d.Replace the impeller. |
3.Excessive power. | a.Service beyond the rated flow. b.Over high suction head. c.Pump bearing worn out. | a.Adjust the flow and lessen the opening of outlet valve. b.Lower. c.Replace the bearing. |
4.Noise and vibration | a.Pipeline not steadily supported. b.Liquid mixed with air. c.Cavitations produced. d.Bearing damaged. e.Motor running overloaded and heated. | a.Fix the pipeline. b.Enhance suction pressure, and exhaust. c.Lower the degree of vacuum. d.Replace the bearing. e.5.Adjustment according to 5. |
5.Motor heated | a.Excessive flow, overloaded operation. b.Scratch. c.Motor bearing damaged. d.Under voltage. | a.Lessen the opening of outlet valve. b.Check for solutions. c.Replace the bearing. d.Stabilize the voltage. |
6.Water leakage of pump | a.Mechanical seal worn out. b.Sand holes or breakage on pump body c.Seal face irregularity. d.Mounting bolts loosened. | a.Replace. b.Weld or replace. c.Repair. d.Fasten. |
